GitHub 주소
JJukE - Overview
JJukE has 4 repositories available. Follow their code on GitHub.
github.com
궁금하신 분들은 놀러오세요!
1. Essential Math for Data Mining

1) Statistics

■ Two main branches of Statistics : 기술 통계학 & 추론 통계학
- Descriptive Statistics (기술 통계학)
- 데이터의 기본적인 특징들을 설명함
- Inferential Statistics (추론 통계학)
- 확률 분포에 대한 특징들을 추론함
(1) Descriptive Statistics (기술 통계학)
- 데이터의 기본적인 특징들을 설명함
- Univariate - 변수 1개
- Mean(산술 평균), Median(중간값), Mode(최빈값)
- Variance(분산), Standard Deviation(표준 편차), Percentile
- Skewness, Kurtosis - tail의 두께
- Bivariate or Multivariate - 이변량, 다변량
- Cross-tabulations and Contingency Tables
- Graphical Representation via Scatterplots
- Quantitative measures of Dependence (Covariance, Correlation)

■ Probability Distribution
- Mathematical function that provides the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes

- Normal Distribution (정규 분포) : 가장 일반적인 연속적인 확률분포 → Bell-shaped
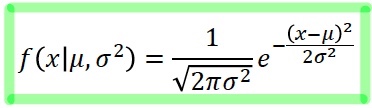
- μ : mean
- σ : standard deviation
- → 두 값에 따라 그래프 모양이 바뀜!

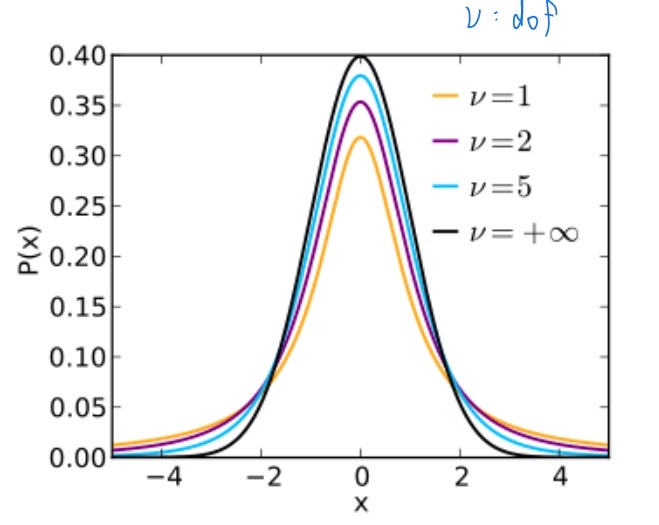
- Student's t-distribution (t-분포) : 추정치의 유효성 검사할 때 많이 사용
Sample mean, Sample variance가 다음과 같을 때,



- Chi-sqaured distribution (카이스퀘어 분포) → 유효성 검증에 많이 사용
X_1, X_2, ... , X_k 가 독립일 때, standard normal random variables Y가 따르는 분포



- F-distribution (F-분포)
X_1, X_2가 각각 d1, d2의 자유도(degree of freedom)를 가지는 chi-squared distribution을 따를 때, Y가 다음을 만족하는 경우 F-distribution을 따름



■ Probability (확률)
- Sampling, Measurement, Error, random number generation
- basic probability
- basic idea, expectation, probability calculus, Bayes theorem, conditional probability
- 확률 분포 함수
- uniform, normal, binomial, chi-square, student's t-distribution, central limit theorem
■ 산점도

2) Linear Algebra
■ Linear Algebra (선형 대수) → 행렬!!
- Linear equations, linear functions, their representations in vector spaces and through matrices
- 수많은 실제 환경에서의 모델링과 그 계산에 유용하게 사용됨
- Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors, Diagonalization, Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
3) Calculus
■ Calculus (미적분)

- Derivative, Partial Derivative 많이 사용
4) Optimization
■ Optimization (최적화)
- 가능한 해 중에서 가장 근접한 해를 구하는 것
- Maximizing, Minimizing
■ 데이터 분석에서 Optimization이 중요한 이유
- 기초적인 데이터 분석 task 중 하나는 각각의 관찰(i)마다 x들을 y에 매핑하는 function f를 찾는 것임
- Learning or Training : 데이터를 기반으로 f를 찾는 과정
- → Learning의 과정에서 Optimization Algorithm이 가장 적절한 f를 찾도록 돕는 tool이 됨
2. Basic Terminologies
■ 배울 내용

1) Types of Learning
(1) Supervised Learning

Output(Answer)을 알고 있음 (→ labeled data)
■ Goal : 새로운 Data 예측
(2) Unsupervised Learning

Output이 없음 (→ unlabeled data)
■ Goal : Input data를 잘 설명할 수 있는 패턴, 그룹, 관계 등을 찾아냄
2) Introduction to Supervised Learning

(1) Types of Data
■ Structured Data
- Values of variable reside in a fixed field
- ex) numeric, date, (male, female), (Mr., Ms., Mrs.), address, ...

- Numeric (Quantitative) (수치형) : number로 표현 가능한 data
- Continuous (연속형) : 값이 무한한 data
- Discrete (이산형) : 셀 수 있는 data
- Categorical (범주형) : 개체가 어떤 group에 속하는지 지칭하는 data (※ Nominal vs Ordinal 구분은 잘 하지 않음)
- Nominal : 범주에 순서가 없음
- ex) (Male, Female), (Class 1, Class 2, Class 3), (Red, Yellow, Green)
- Ordinal : 범주에 순서가 존재함
- ex) Score : A+, A, A-, B+, B, B- , ... // Size : S, M, L, XL, XXL, ...
- Nominal : 범주에 순서가 없음
EX) the input to a data mining:

■ Unstructured Data → 알고리즘을 바로 적용하기보다 Structured Data로 변환한 후 적용함
- Values of variable do not reside in a fixed field (→ 정해진 format이 없음)
- ex) documents, webpages, images, videos, ...
■ Data Set의 예 : 보통 input data set은 여러 독립적인 instance들의 set으로 표현됨

(2) Regression vs Classification
■ Regression

■ Classification

(3) Process of Supervised Learning

2) Unsupervised Learning
(1) Clustering
■ Grouping Data Points

(2) Dimensionality Reduction
■ Dimensionality Reduction

(3) Association Rule Mining
→ 연관된 data에서 규칙을 찾음
■ Finding useful information from transactions (대표적인 예 : 장바구니 분석)

- 유용한 정보의 예 : "If item A ⇒ item B" → Association Rule
- 함께 구매가 될 것 같은 상품들의 쌍을 찾음!
Overall Description









최근댓글